Formatting a drive in Windows is usually a straightforward process, but sometimes you might encounter the “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” error. This can be a frustrating issue, especially when you need to clear data or prepare a drive for use.
This article explores what this error means, its common causes, and provides detailed solutions to resolve it on Windows 7, 10, and 11. Additionally, it covers how to force Windows to format a drive using Command Prompt (CMD) and other shortcuts.
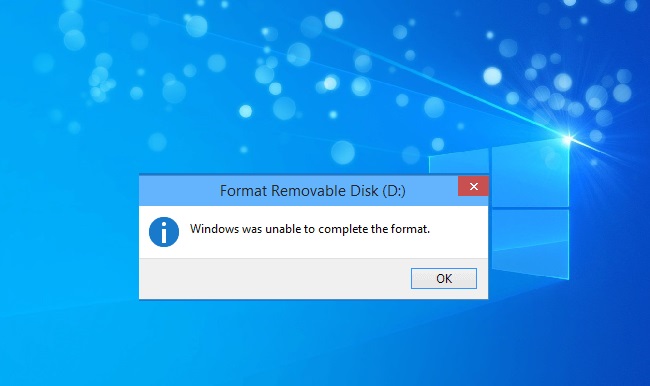
Understanding the “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” Error
When Windows is unable to format a storage device, it typically displays an error message: “Windows was unable to complete the format.”
This error can occur with any type of storage media, including hard drives, SSDs, USB flash drives, and SD cards. It indicates that something is preventing Windows from initializing the formatting process on the selected drive.
Common Causes of the Error
Several factors can lead to this error on Windows 7, 10, and 11:
- Drive Is Locked: The drive might be in use by another process, or it might be write-protected.
- File System Issues: Corruption within the file system that cannot be resolved during the format process.
- Physical Damage: The drive may have physical damage, preventing it from being formatted.
- Outdated or Corrupted Drivers: Drivers that are not up-to-date or have become corrupted can interfere with the ability to format.
- Virus or Malware: Malicious software can prevent drives from being formatted to protect itself.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix the Error
Step 1: Ensure the Drive Is Not In Use
- Close all programs that might be using the drive. Check the Task Manager for any active processes that might be accessing the drive and terminate them.
Step 2: Check for Write Protection
- Ensure the drive is not write-protected. For USB drives or SD cards, check the physical write-protection switch and make sure it is set to allow writing.
- For internal drives, you can use the DiskPart tool to check status:
diskpartlist diskselect disk [number]attributes disk
If the disk is write-protected, remove it using
attributes disk clear readonly.
Step 3: Scan for Malware
- Use your antivirus software to scan the drive for viruses or malware that could be preventing the format.
Step 4: Update or Reinstall Disk Drivers
- Go to Device Manager, right-click on the disk under “Disk drives,” and select “Update driver.” If that does not work, try “Uninstall device,” then restart your computer to reinstall the drivers automatically.
Step 5: Use Disk Management to Format the Drive
- Open Disk Management by right-clicking on “This PC” or “My Computer,” select “Manage,” then “Disk Management.”
- Right-click on the drive you wish to format and select “Format.” Choose your desired file system and proceed.
How to Force Windows to Format a Drive Through CMD
If you’re unable to format a drive through the standard interface, you can use CMD to attempt a force format.
Using CMD to Format a Drive
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Enter DiskPart by typing
diskpart. - List all disks by typing
list disk. - Identify the disk you want to format (be very careful to select the correct one as this process is irreversible).
- Select the disk by typing
select disk X(replace X with the correct disk number). - Clean the disk by typing
clean. - Create a new primary partition by typing
create partition primary. - Format the disk by typing
format fs=ntfs quick(replace NTFS with your desired file system if different). - Assign a drive letter by typing
assign.
Further Techniques for Troubleshooting Drive Formatting Issues on Windows
If you’ve gone through the initial steps and are still facing challenges with formatting your drive, here are additional advanced troubleshooting techniques to help you resolve the “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” error on Windows 7, 10, and 11.
Check for Bad Sectors
Drives with bad sectors or physical damage can often cause formatting errors. To check and repair bad sectors on your drive:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type the command
chkdsk E: /f /r /xand press Enter. Replace “E” with the letter of the drive you want to check. This command will force the drive to unmount, fix any found errors, locate bad sectors, and recover readable information. - Wait for the process to complete and try formatting the drive again.
Use Third-Party Formatting Tools
Sometimes, third-party tools can manage to format drives that Windows cannot. Tools like GParted (for bootable USB creation), EaseUS Partition Master, or MiniTool Partition Wizard offer robust formatting options and user-friendly interfaces that might successfully format your drive.
Formatting via BIOS
In some cases, adjusting BIOS settings to change the mode of the SATA controller might resolve issues, especially for internal drives:
- Restart your computer and enter BIOS settings (usually by pressing F2, F10, DEL, or ESC immediately after turning on the computer).
- Navigate to the Storage or Advanced tab and find the SATA configuration.
- Switch between available modes (e.g., AHCI, RAID, IDE) to see if another mode allows you to format the drive. Be aware that changing SATA modes can affect the operating system’s ability to boot, so this should be done with caution.
Re-initialize the Disk
If the disk is showing as “Unknown” or “Not Initialized” in Disk Management, it might need to be re-initialized:
- Open Disk Management (right-click on “This PC” > “Manage” > “Disk Management”).
- Right-click on the disk that shows as unknown or not initialized, and select “Initialize Disk.”
- Choose either MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table) as the partition style, and proceed.
- After initialization, try formatting the disk again.
Adjusting Group Policy Settings
For network administrators or users within an organization, group policy settings might restrict disk management capabilities:
- Open the Group Policy Editor (type
gpedit.mscin the Run dialog). - Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access.
- Ensure that settings such as “All Removable Storage: Allow direct access in remote sessions” are configured properly to allow formatting.
Reset Windows
As a last resort, if all else fails and the drive is crucial, consider backing up your system and performing a system reset or reinstalling Windows. This can resolve deep-rooted software issues affecting drive formatting:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Click on “Get started” under Reset this PC.
- Choose to keep or remove your files, and follow the instructions to reset your system.
Conclusion
The “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” error can be resolved by following the outlined steps carefully. Always ensure that you back up any important data before attempting to format a drive, as this process will erase all data.
With the right approach, you can overcome this error and prepare your drive for use on Windows 7, 10, or 11. Regular maintenance, such as updating drivers and scanning for malware, can also help prevent such issues from recurring.
FAQ: Troubleshooting “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” Error
Q1: What does the error “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” mean?
A1: This error indicates that Windows was unable to complete the formatting process for a specific drive. It can occur due to various issues, including file system corruption, drive write protection, physical damage, or software conflicts.
Q2: What are the most common causes of formatting issues in Windows?
A2: Common causes include:
- The drive being locked or in use by another process.
- Write protection being enabled on the drive.
- File system errors or corruption.
- Outdated or corrupted device drivers.
- Interference from antivirus or security software.
Q3: How can I fix a drive that won’t format on Windows 10/11?
A3: To fix a drive that won’t format:
- Ensure no files from the drive are in use.
- Check and disable write protection.
- Update or reinstall device drivers.
- Run CHKDSK to repair file system issues.
- Use Disk Management to attempt a format, or use the DiskPart tool in Command Prompt for more control.
Q4: How do I force Windows to format a drive using CMD?
A4: To force format a drive using CMD:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type
diskpartand press Enter. - Enter
list disk, identify your drive number. - Type
select disk X(replace X with your drive number). - Type
cleanto wipe the drive. - Create a new partition with
create partition primary, then format it withformat fs=ntfs quickor another file system of your choice.
Q5: How do I refresh OneNote to sync correctly?
A5: To refresh OneNote:
- Open OneNote and go to the “File” tab.
- Click on “Info” then “View Sync Status”.
- Click “Sync Now” for each notebook that needs to be refreshed.
Q6: How can I automatically sync OneNote?
A6: OneNote automatically syncs by default. Ensure you are connected to the internet and signed in to your Microsoft account. You can manually check sync settings by going to “File” > “Options” > “Save & Backup” and adjusting the settings under “Sync notebooks automatically.”
Q7: How do I sync OneNote offline?
A7: Work in your notebooks normally while offline; OneNote will store changes locally. Once you reconnect to the internet, OneNote will automatically sync your changes.
Q8: How do I restart OneNote on Windows?
A8: Close OneNote completely, then reopen it. Ensure it’s not running in the background by checking Task Manager.
Q9: How do I clear the OneNote cache to fix syncing issues?
A9: To clear the OneNote cache:
- Close OneNote.
- Navigate to
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\OneNote\16.0\cache(adjust the version number as necessary). - Delete all files within this folder.
Q10: Can I change the file system during the formatting process?
A10: Yes, during the formatting process, you can choose a different file system such as NTFS, FAT32, or exFAT, depending on your needs and the limitations of the drive.
These FAQs aim to equip you with the knowledge to troubleshoot and resolve the “Windows Cannot Format This Drive” error, ensuring you can manage and maintain your drives effectively in Windows environments.



